



Method to produce ringed, adjustable mesh ! !, (Newer ring production experiments).
The First Ringforcement Page Follows
Research by Bo Atkinson
A postulated synergy of ferocement, concrete, masonry and curved construction,
a combined building method. The advantages of each of these old materials
and methods are brought together into one sculptural building system. Ringforcement
is a specialized rethinking of cement reinforcement.The specific components
may vary somewhat depending on local availability of materials, at a given
construction site. Nonlinear, small scale building as in the dome example
below are suggested applications for Ringforcement. A flat spiral form
under consideration may be seen
here. More advanced applications would include freeform
structures and alterations unavailable from air form molds for structuring.
The method may fit within the "monolithic" definition, providing
cement application is properly completed in one continuous step before
curing.
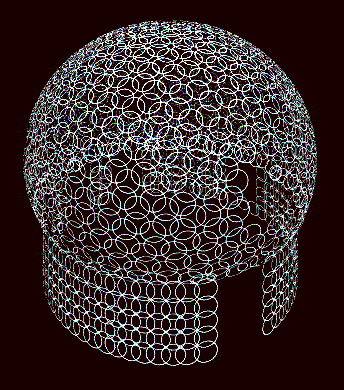
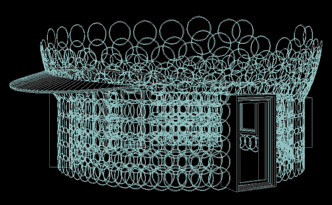
Above: Position of rings used as reinforcement in dome building, (seen from above). The dome was modeled in a minimal size to economically provide for essentials. (The size is about 20 ft. or 6.1 m in diameter). This particular, conceptual approach to building resulted over a 25 year period, of free minded concrete sculpting experimentation, by the author himself. This is a conceptual presentation only. The mentioned sculptural aspect is a specialized building method which emphasizes experimenting with concrete tooling. (For more on this tooling, see links below).
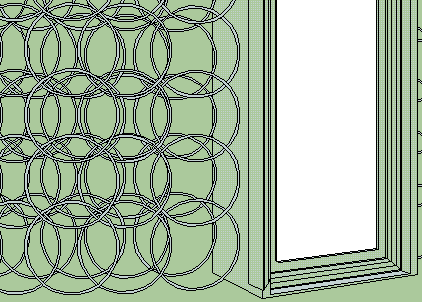
Pre existing ferrocement methods notably use mesh for reinforcement of skin like shells. Mesh implies continuous, fixed linkage between mesh elements. Ringforcement newly proposes "untied" rings as an alternative. Ferrocement depends on the mesh to provide a base on which to apply cement. Ringforcement combines the traditional masonry base of stone and the newly proposed ring, (one nonlinear row at a time) as a base for building up structure. However, Ringforcement uses a much broader selection of graded aggregates than masonry or concrete. These are thoroughly coated with cement paste, as in normal concreting, but rarely the case with masonry. Masonry typically omits intermediate stones from masonry stone size, all the way down to sand particle. Yet it is this continuous grading of aggregate particles which economically improves ultimate strength for cement mixtures. Emphasis on this unusual synergy allows vertical building progress without the slumping tendency of ordinary, freshly mixed concrete and also without the masonry focus of close packed bricks or large faced stones. The mission of Ringforcement is to attempt a new synergy of materials. It is secondarily an attempt to extend aggregate size ranges. Primarily, it is the employment of rings as the choice of reinforcement. The method invites all scales of implementation.
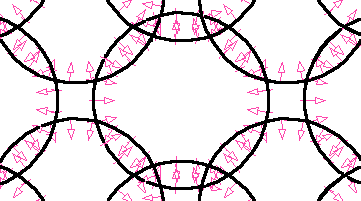
Above: "Compressive Chain", Black rings overlap to create zones which "inter- loop" . Compressive units of embedded concrete bind overlapping rings. The red arrows indicate compression zones for individual rings. The overlap of compression zones, between neighboring rings, results in an extension of tensile strength over the whole of the constructed element.
Linear reinforcement rods are recommended along perimeters and outlines, as in normal concrete practice. The author has found that overlapping rings provide the same strength levels as mesh reinforcement provides. The casual, testing methods used were believed reliable in that mesh tests are generally unofficial, since mesh qualities vary. The testing referred to was breaking up old work by hammer and noticing the relative strength levels. The overlapping of rings in a concrete body, transmits the tensile property of reinforcement steel from one ring to the next. In compound curves, this is significant, since mesh is planar, (that is: it cannot be elastically formed without kinks which cancel the chief tensile property). Compound curves are structurally advantageous, reducing the surface area required to enclose a given space. Through curviture, cost may be reduced, (synergy). Without breaking a budget, sculptural qualities are also possible.
Is this new? Compressive linkage for rings is new, only in that the author has not noticed this particular approach published, nor discussed, nor suggested before. Structuring
What are some advantages?
These advantages are available where gravel is minded and labor is willing. Advanced tooling development is a another possibility.
Advantages over concrete are 1) reduced concrete form work, 2) ease of reinforcement placement, 3) less shrinkage during curing 4) unrestricted curvilinear possibilities 5) lighter shell practicalities, 6) use of rawer material, hence savings through local economies, 7) combined monolithic-structure and finish process in one (flowing) step.
Advantages over mesh formed ferrocement include: 1) ease in thorough cement
coating of all metal reinforcement surfaces. By contrast, penetration of
overlapping meshes of ferrocement is more difficult. 2) Meshes costs more
industrial effort to produce. Rings could be efficiently mass produced,
or alternatively flat wire spirals offer testing insights. 3) Shipping,
and mass handling of rings, rods or wire is simpler than restrictively
sized mesh products.
Disadvantages?
This synergy presents several issues which are difficult to implement. Foremost is trying anything which departs from traditional labor practices, E.G.: mixing concrete with unusual aggregates. Traditional equipment does not ideally lend itself to the task. This suggests either extra man hours where labor methods are used. However new experimental equipment concepts are available. (Links below).
A limitation for small crews is the allowable progress with "green" (uncured ) cement. For nearly vertical walls, a single story is possible in one or two days. But sloping beyond several degrees requires additional support. Ringforecement might or might not apply to overhead flooring with an integrated joist- flooring system.
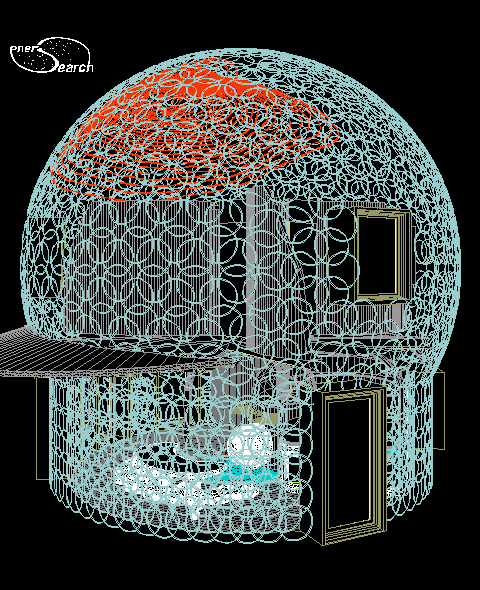
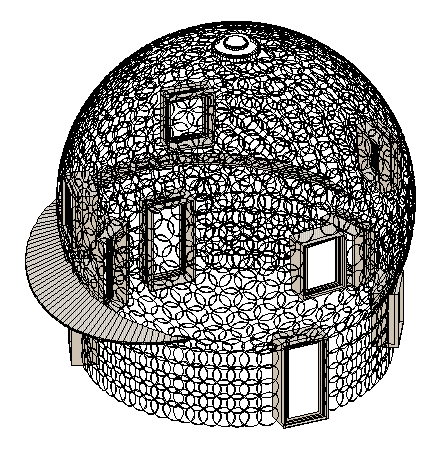
Above: Same CAD dome model shown above. Two sets of rings are shown for two layers of ferro concrete, on the first story wall. The two layers sandwich thermal insulation, which is not shown. The curved dome surface is represented by just one layer of rings in this rendering.
Variations Of Ring Sizes
The paragraphs and pictures above might be mistaken to imply : "one ring size fits all". Rather, multiple sizes of rings are intended for your consideration. Small rings could conceivably replace some of the large aggregate. Certain localities may not have cheap concrete aggregate readily available, substitutes might be explored. An alternative ring design might utilize several ring sizes, or denser coverage of rings. Denser ring coverage (or more rings per unit of area) would call for rings of thinner gage. This idea opens additional exploration of experiments with rings as a more refined replacement for aggregates, indeed graded ring sizes in the manner of concrete aggregates. The efficacy here depends on comparative shipping costs, between steel and stone, which for some areas, could favor the use of greater proportions of rings. Non metallic rings are also a possibility.
A 3D Ring Matrix:__Here is a link to some further developments with cell like reinforcement.
Wall with contoured surface and ringed tessellations is tested.(October 2000).
Pictures of preliminary strength testing during summer of 2000.
Sprayed Monolithic (Balloon Formed) Domes Considered
Admittedly the author has sprayed concrete structures no larger than 12 ft to 4 meters, (using jury rigged small compressor equipment). This much is assumed: House sized spraying requires expensive equipment and is limited by the relatively few form sizes and configurations which are seamed together. Ringforcement as aggregate might adapt to airform spaying.
Materially, the sprayed concrete generally has small aggregate which increases the spray price for a given thickness. Other placements methods can economize on cement paste costs and achieve equal strengths. (This is truer for localities which have gravel mining or benign mineral dumps within reasonable trucking distance).
Pumped Concrete
Concrete pumping is an already existing, widely available service which can be applied to ringforcement. It has a limitation on the size of stone which can be pumped. This size limitation might loose some cost advantages offered by larger stone particles. It might also introduce more difficulties in work scheduling, (in the case of small operations). Structural concrete work always demands intense concentration but is more intense when more than one contractor is needed to coordinate schedules.
Other Materials
The use of plastic, fibergalss or other high tensile strength materials is plausible. Composite materials are a credible application for ringforcement. The essential concept remains the same: high tensile rings combined with low cost compressive "filler" material. The rings are "chained" by compressive linking instead of by tensile continuum. Therefore a new concept of "compressive chaining" is formed. Enersearch would like research into ring manufacturing technology: how to "extrude" rings out of appropriate materials instead of using wire like base materials.
The content on this website, http://harmoniouspalette.com, is placed in the public domain only as a free exchange of ideas and as a "hard studied wish to serve life". The author assumes no responsibility for the improper use of the concepts in these web pages, as all relevant laws of life and local codes should be verified and observed before any building or experimentation proceeds. discussion is welcome, please write. Bo Atkinson